How To Search Google Scholar For Systematic Review

Google Scholar alone has not been shown to retrieve more.
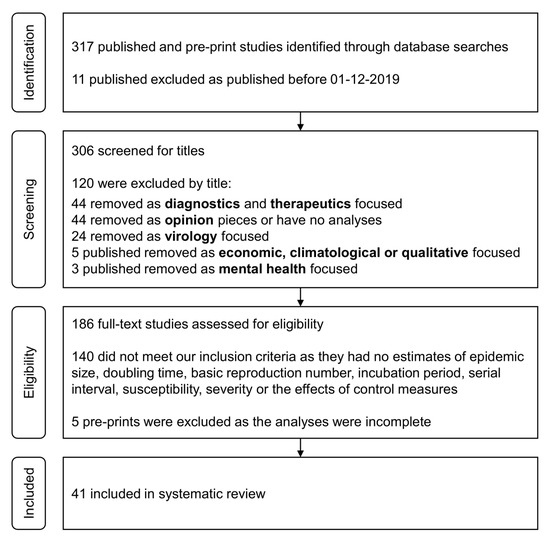
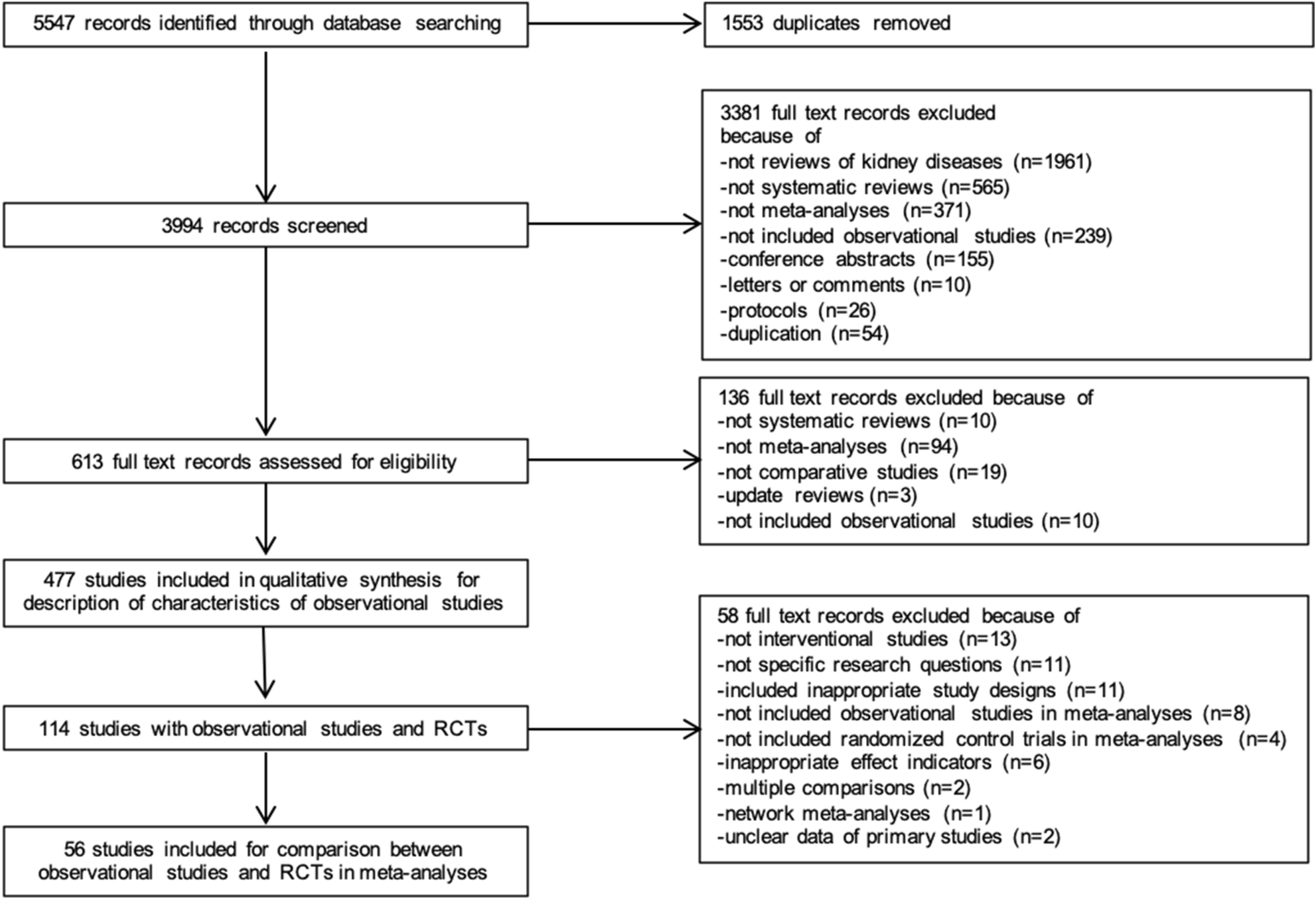
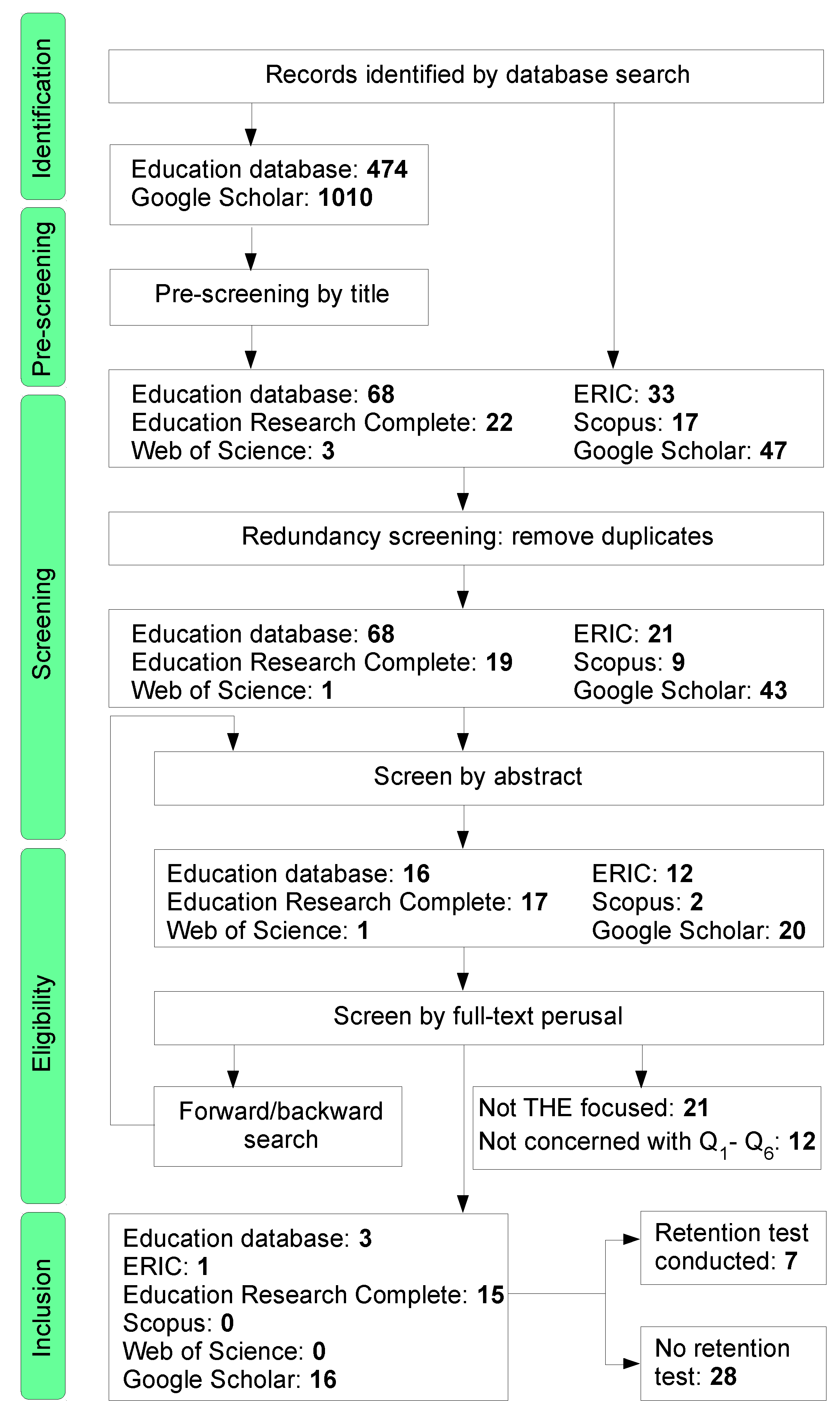
How to search google scholar for systematic review. Systematic reviewmeta-analysis steps include development of research question and its validation forming criteria search strategy searching databases importing all results to a library and exporting to an excel sheet protocol writing and registration title and abstract screening full-text screening manual searching extracting data and assessing its quality data. The search algorithm is not known and cannot be controlled Google adapts the search to each user in order to personalize information and as a result a systematic search is quite probably not replicable. I advice you to use databases like WebofScience or Scopus for example and use Google Scholar.
Google Scholar is a useful tool for finding research literature. This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. Conclusion The coverage of GS for the studies included in the systematic reviews is 100.
I searched PubMed in the most amusingly obvious way. Both subject headings and keyword searching in the databases that allow this and searching multiple databases where articles may be indexed differently or a very similar search. To ensure adequate performance in searches ie recall precision and number needed to read we find that literature searches for a systematic review should at minimum be performed in the combination of the following four databases.
To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts bookmark a search results page with the desired selection. One approach is to resort to the use of Boolean search queries and expressions. Ad Stop using clunky tools and enable your whole review team to collaborate from anywhere.
Contrary to Gehanno et als conclusions that GS could even be used alone 16 we found that GS was not up to the required search standard for systematic reviews. By combining keywords with Boolean operators and appropriate use of parentheses it is possible to construct search queries of arbitrary complexity. To be practical therefore most systematic reviewers will create search strategies that are precise enough for them to able to cope with the number of results that are returned but use different methods of searching eg.
Click on My library at the top of the Google Scholar homepage or in the left column of a search results page to view all the articles in your library. If used in systematic reviews for grey literature we recommend that searches of article titles focus on the first 200 to 300 results. This video shows a few tips and tricks for how to find academic literature using Google Scholar.